MapReduce Working and Components in NCache [Deprecated]
MapReduce in NCache allows developers to process huge amounts of unstructured data in parallel across an NCache cluster. To distribute input data and analyze it in parallel, MapReduce operates in parallel on all nodes in a cluster of any size.
MapReduce is a programming model for processing and generating large data sets with a parallel, distributed algorithm on a cluster. The term “MapReduce” refers to two distinct phases. The first phase is the ‘Map’ phase, which takes a set of data and converts it into another set of data, where individual items are broken down into key-value pairs. The second phase is the ‘Reduce’ phase, which takes the output from the ‘Map’ as an input and reduces that data set into a smaller and more meaningful data set.
A user-defined Mapper processes a key-value pair to generate a set of intermediate key-value pairs. Reducer processes all those intermediate key-value pairs (having the same intermediate key) to aggregate, perform calculations, or any other operation on the pairs. Another optional component, Combiner, performs the merging of the intermediate key-value pairs generated by the Mapper before these key-value pairs can be sent over to the Reducer.
The following example illustrates a MapReduce task (with and without Combiner) being executed over a cluster of three nodes. The task takes orders as input to the Mapper and extracts the count of products consumed in it.
- In Figure 1, the Mapper’s output is directly sent to the Reducer and is aggregated on the Reducer’s node.
- In Figure 2, the count over a single node is aggregated first and this aggregated count is sent to the Reducer node for the final aggregation.
MapReduce without Combiner:
In the following figure the Mapper’s output is directly sent to the Reducer and is aggregated on the Reducer’s node.
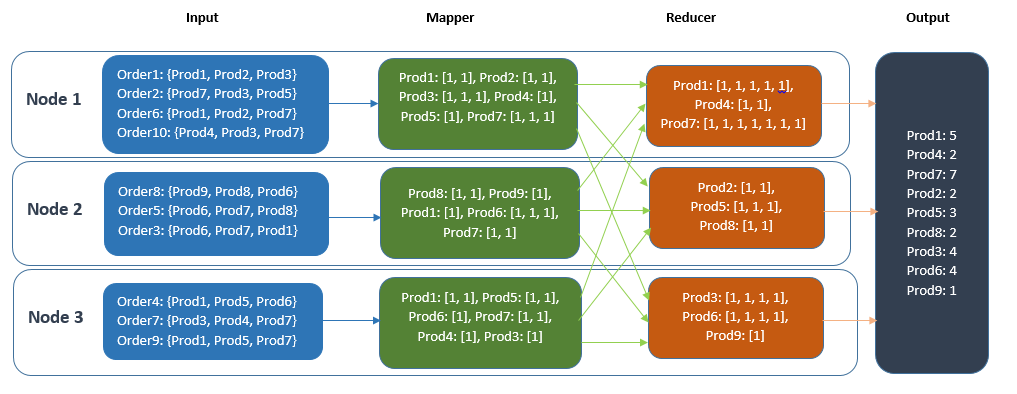
MapReduce with Combiner:
In this figure the count over a single node is aggregated first and this aggregated count is sent to the Reducer node through Combiner node for the final aggregation.
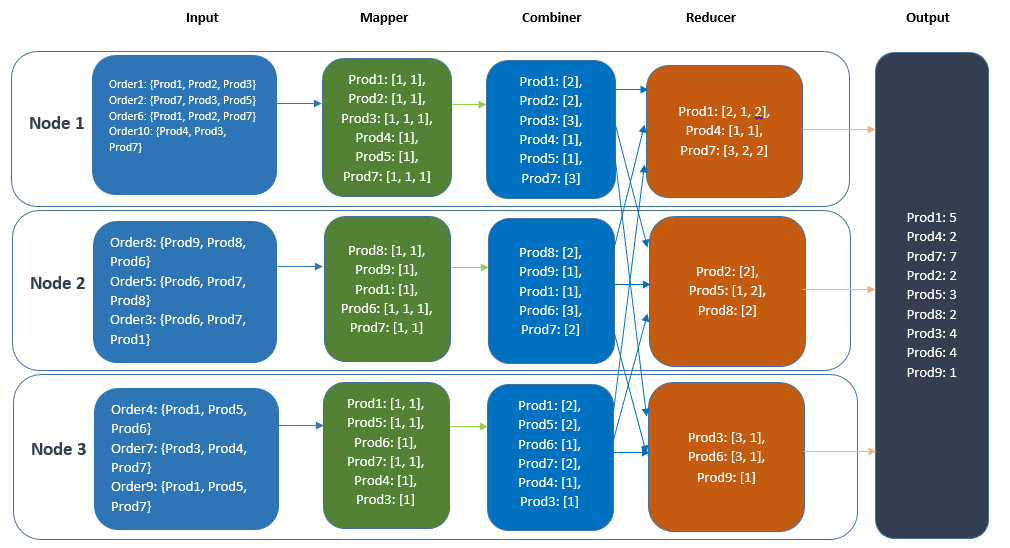
How does MapReduce Work?
Generally, MapReduce consists of two (sometimes three) phases: i.e. Mapping, Combining (optional) and Reducing.
- Mapping phase: Filters and prepares the input for the next phase which may be Combining or Reducing.
- Reduction phase: Takes care of the aggregation and compilation of the final result.
- Combining phase(Optional): Responsible for the reduction local to the node, before sending the input to the Reducers. This phase optimizes the performance as it minimizes the network traffic between the Mapper and Reducers by sending the output to the Reducer in chunks.
Similarly, NCache MapReduce has three phases: Map, Combine, and Reduce. Only the Mapper is necessary to implement, Reducer and Combiner implementations are optional. NCache MapReduce will execute its default Reducer if the user does not implement Reducer. Default Reducer merges output omitted by the Mapper into an array.
The Mapper, Combiner, and Reducer are executed simultaneously during an NCache MapReduce task on the NCache cluster. Mapper output is individually sent to the Combiner. When the Combiner’s output reaches the specified chunk size, it is then sent to the Reducer, which finalizes and persists the output.To monitor the submitted task, a traceable object is provided to the user.
The number of tasks to be executed simultaneously and the Mapper’s output chunk is configurable. The Mapper’s output is sent to the Combiner or the Reducer once the output chunk reaches the configured chunk size. See NCache Administrator’s Guide.
Components of a MapReduce
A typical MapReduce task has the following components:
Mapper: Processes the initial input and enables the user to emit the output into a dictionary to be used as an input for the Combiner or Reducer.
Combiner Factory: Creates and manages Combiners for each key emitted into the output by the Mapper.
Combiner: Works as a local Reducer to the node where the Mapper’s output is combined to minimize the traffic between the Mapper and the Reducer.
Reducer Factory: Create and manage the Reducers for each key emitted into the output by the Mapper or the Combiner.
Reducer: Processes all those intermediate key-value pairs generated by the Mapper or combined by the Combiner to aggregate, perform calculations, or apply different operations to produce the reduced output.
Key Filter: Key Filter, as the name indicates, allows the user to filter cache data based on its keys before it is sent to the Mapper. The KeyFilter is called during the Mapper phase. If it returns true, the Map will be executed on the key. If it returns false, the Mapper will skip the key and move to the next one from the cache.
TrackerTask: This component lets you keep track of the progress of the task and its status as the task is executed. It also lets you fetch the output of the task and enumerate it.
Output: The output is stored in memory, on the server side. It can be enumerated using the TrackableTask instance on the client application.
Warning
This feature is only supported till 5.3 SP4.
See Also
Sample Implementation of MapReduce
Using MapReduce in Cache
Aggregator
Entry Processor
Configure MapReduce