Using SQL Queries with Distributed Cache
Author: Iqbal Khan
NCache lets you create a distributed cache in the middle-tier so you can reduce expensive trips to the database and greatly improve your application performance. It also enhances scalability by allowing frequently accessed data to be served from a highly scalable cache, rather than relying on a single database server.
Your application typically uses a cache as a Hash table where everything is stored based on a key, and you must have this key to fetch an item. This is like having a relational database where you can only use the primary key to find data. While this method is effective in many cases, complex applications typically require data retrieval based on attributes beyond just the primary key. And, since you're keeping a lot of your data in the cache, it would be very useful if you could search the cache in this manner as well. NCache provides exactly such a facility.
In this article, I will discuss how SQL querying works in NCache.
Executing SQL Queries in NCache
NCache allows you to query cached data using SQL-like syntax. Instead of relying solely on primary keys, you can filter cached objects based on specific attributes, such as ProductID, Category, or Price. The following code shows how you can perform a cache query in your .NET application.
// Precondition: Cache is already connected
// Items are already present in the cache
// Create a query that will be executed on the dataset
// Use the Fully Qualified Name (FQN) of your own custom class
string query = "SELECT * FROM FQN.Product WHERE ProductID > ?";
// Use QueryCommand for query execution
var queryCommand = new QueryCommand(query);
// Providing parameters for query
queryCommand.Parameters.Add("ProductID",50000);
// Executing QueryCommand through ICacheReader
ICacheReader reader = cache.SearchService.ExecuteReader(queryCommand, false, 0);
// Check if the result set is not empty
if (reader.FieldCount > 0)
{
while (reader.Read())
{
string result = reader.GetValue<string>(0);
// Perform operations using the retrieved keys
}
}
else
{
// Null query result set retrieved
}The above code executes a parameterized query on the cache to find products with a ProductID greater than 50000. It uses a QueryCommand to pass the query and its parameters, and ExecuteReader to retrieve matching keys through an ICacheReader. The loop reads each result one by one, allowing efficient iteration over matching entries without loading the entire data at once. If individual objects are needed, a separate fetch operation using each key would be required.
In addition to retrieving, NCache also allows you to delete cached data using SQL-like DELETE queries. However, INSERT and UPDATE operations are currently not supported.
Indexing Searchable Attributes
Please note that NCache requires all searchable attributes to be indexed. This is because without indexing, NCache would have to traverse the entire cache to find the items the user is looking for. And that is a very costly operation with the potential of slowing down the entire cache and undoing the major reason why people would use NCache, namely, to boost their application performance and scalability.
NCache provides two ways to define these indexes:
- Define indexes programmatically.
- Configure static indexes through the NCache Management Center.
Querying Different Caching Topologies
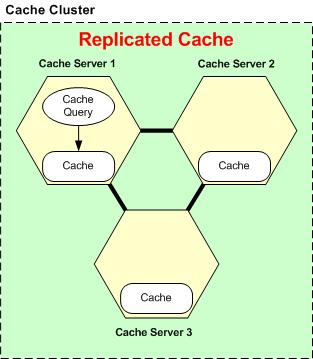
Although the search behaviour from the client application's perspective is the same regardless of what caching topologies you're using, the underlying search behavior varies from topology to topology. For example, if you're searching for a Replicated cache, your search is conducted entirely on the cache server you initiated this search from. This is because the entire cache is available there. Here is how a query is run in a Replicated Cache.
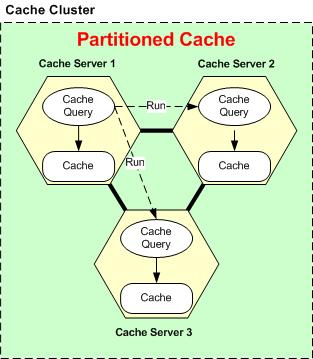
However, if you have a Partitioned or Partition-Replica caching topology, then data is divided among all the nodes in the cluster. In this situation, the cache server where the query is initiated sends the query to all other servers in the cluster and also runs it locally. The query then runs in all servers in parallel, and its results are returned from all the nodes to the originating server node. This server node then combines all the results (does a "union") and returns them to the client. Below is a diagram showing all of this.
Query Using SQL Projections
NCache enables you to retrieve either all the indexed attributes of a class or only specific projections from the cache store using SQL-like queries. These projections are designed to support efficient searching and play a vital role in optimizing query performance. For example, if you only need the available units column for products within a particular category, you can use a query like the one below:
SELECT UnitsInStock FROM FQN.Product WHERE Category = "Sample_Category"By selecting only the required columns, you avoid the overhead of fetching all indexed attributes of the class. This approach improves query execution and helps maintain overall performance, allowing NCache to deliver faster and more efficient results.
Conclusion
As you have seen, NCache makes it very simple to query the distributed cache. This is a powerful feature that allows you to use your cache in a more meaningful way and find things more easily.
What to Do Next?
Author: Iqbal Khan works for Alachisoft , a leading software company providing .NET and Java distributed caching, O/R Mapping and SharePoint Storage Optimization solutions. You can reach him at iqbal@alachisoft.com.