AppFabric vs NCache Comparison (Video)
This video demonstrates a comparison between AppFabric v1.1 and NCache. It describes major feature differences between both products. For a detailed comparison, please read the comparison document.
Main Uses of NCache
Today I will go over a comparison between NCache and Microsoft AppFabric. Before I get started, let me give you a brief introduction to NCache. There are three ways that you can use NCache.
- Object Caching: First is object caching, where you improve your application performance and scalability, by reducing those expensive database trips and making sure that database never becomes a bottleneck.
- Caching Solution: The second is to use NCache as a reliable and scalable cache for ASP.NET application in three different areas. One is to store your session state in a web farm in NCache. Second is to store your output cache in a web farm, and third is destroy your views view state in NCache in a web farm. Most importantly the session state storage is a very popular feature of NCache.
- Runtime Data Sharing: The third way the NCache is used is to do runtime data sharing between applications in a publish/subscribe data sharing model.
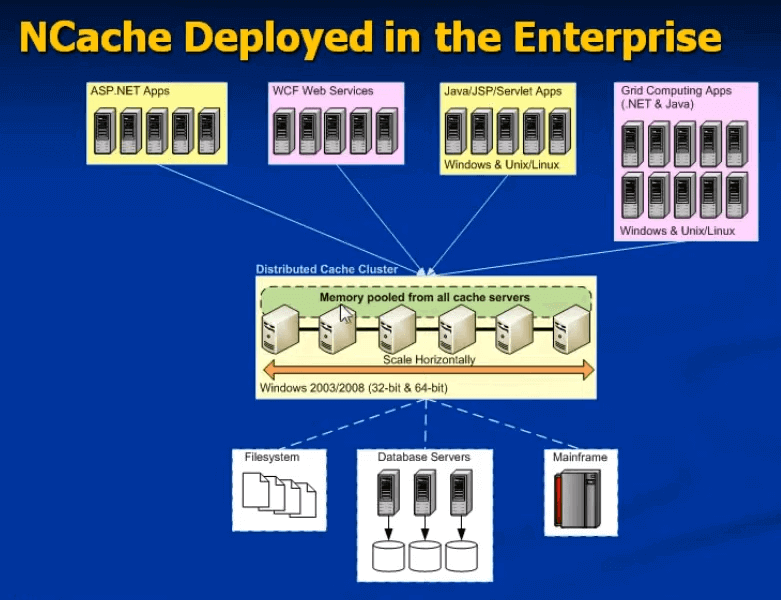
NCache Deployment
Here is a typical deployment of NCache in an enterprise. You can build a common caching tier for all your applications with aminimum of two cache servers for redundancy. Or, you can have a separate caching tier for each application that is your choice. The caching tier is usually a 64-bit platform because it can have more memory even though your applications might be 32-bit, and you don't have to have a separate cache tier. You can run the cache server on the same box as your web or application server.
NCache vs AppFabric
So, here are the areas where NCache differs from Microsoft AppFabric. There are seven areas.
- Product Maturity and Support Model
- Cache Performance and Scalability
- High Availability of the Cache
- Caching Topologies
- Graphical admin and Monitoring tools
- Important NCache features (not in AppFabric)
- Native Java Support
Product Maturity and Support Model
So, in the product maturity and support model, NCache has been in the market for about seven years. The current version is 4.1, which is the 9th version of the product. It's a very stable and mature product. On the other hand AppFabric is version 1.1. So, it's a second version in the market. And, on a support model NCache offers regular and 24x7 support options. You can purchase support with NCache. And, especially in a 24x7 support, you can call us day or night if you have any issues especially production type of issues, and you know, that type of a support, you know, can really help your business, if you have any problems.
Performance and Scalability
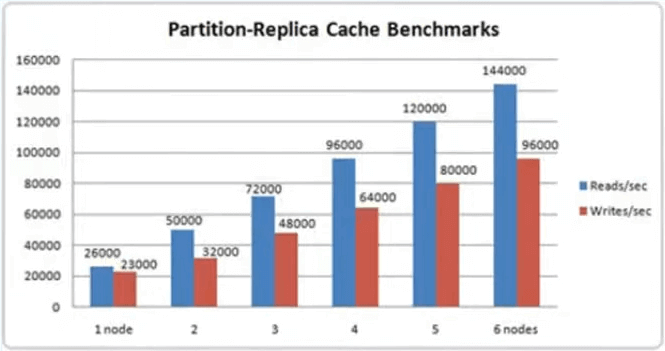
Another area is the cache performance and scalability. As you know, the most important reason you would use the distributed cache is to improve application performance and scalability. NCache in this area is faster and more scalable than AppFabric. Our internal benchmarks show a noticeable difference. And, you can also do your own benchmarking. We give you a stress test tool, and you can see how much faster NCache is.
Here's a glimpse of some of the benchmarks. In a 2 node cache cluster you have 50,000 reads per second and 32,000 writes per second as you can see it increases in the linear fashion.
High Availability of the Cache
The other area is high availability of the cache. The cache runs in your data center therefore you cannot afford for the distributed cache to go down. NCache provides you 100% uptime because it has a self-healing peer-to-peer cluster architecture. When we use the word cluster we do not mean windows clustering, we have our own TCP-based cache cluster, and this cluster has no single point of failure. This means that you can add or remove any server from the cache cluster. There is no master or slave everybody is up here. So, this makes NCache highly dynamic.
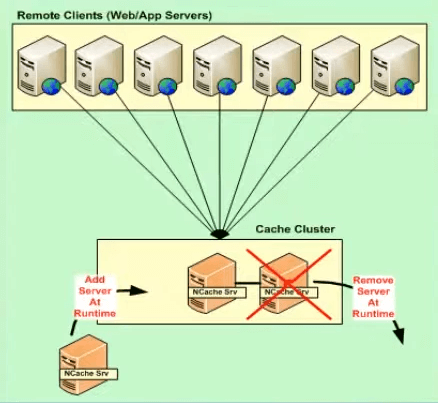
AppFabric on the other hand has a master slave cluster architecture, and also it has a single point of failure in the config file storage which you can overcome by storing the configuration in a SQL server cluster. But, again the AppFabric itself does not provide capability which NCache does.
Caching Topologies (Client Cache)
Caching topologies are basically ways that you store data in the cache and also your connection strategies. NCache has rich set of caching topologies. To get more details about each of these topologies, please watch the video about NCache Architecture on our website. But, just to mention we have mirrored cache, which is a two node active-passive topology. We have replicated cache which is good for reference data. We have partitioned cache which partitions the cache across multiple servers, and we have partition replicas cache which is a combination of partitioning and replication, but does a very intelligent replication. So, even if you have more than two servers there’re only two copies of the cache. It's our most popular caching topology.
And then we have a Client Cache which, although AppFabric also claims to have a client cache but their is a standalone local cache. Our client cache actually synchronizes with a cache cluster, and I will talk a little bit about that.
Here's the client cache NCache has. So, if you were to have a caching cluster here. The client cache would actually sit on your web app or application server box. It's a local cache but it is connected to the clustered cache. What that means is, whatever data is in the client cache if that data changes in the cluster cache the clustered cache notifies the client cache so it can update itself.
The other part of the client cache that's really cool is that you don't have to do any special programming for it, you just plug it into a configuration.
Bridge Topology (for WAN Replication)
Another area that NCache has is called bridge topology for WAN replication. If you have multiple data centers, multiple geographical locations, either for disaster recovery or multiple active data centers, you can use the bridge topology to replicate the cache across the WAN in an asynchronous fashion without slowing down the caches on either side. So, what happens, let’s say, whatever you update here, gets queued up in the bridge, the bridge makes the same changes in the target cache in an active-passive. In an active-active the bridge is two ways. So, both sides can make changes in it and apply them to the other side.
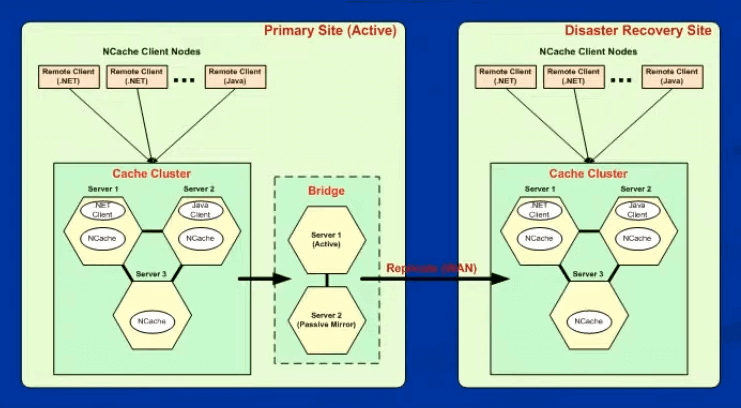
In an active-active there's a conflict resolution logic in NCache bridge that automatically resolves conflicts, or you also provide a conflict resolution handler that can resolve conflict. So, there's an active-passive, active-active, hub spoke, in which there's one center and multiple passive satellite caches, and a star topology in which there's one center and multiple active satellite topologies or caches.
Admin and Monitoring Tools
Another area is graphical admin and monitoring tools. NCache has very easy to use tools. Let's say there's an NCache manager which is a GUI based tool that lets you configure and administer cache clusters from a single location. There is a NCache monitor, lets you monitor cache activity at runtime. There’re a bunch of command line tools that you can use in scripting. There are a lot of PerfMon Counters. There’re a bunch of events that NCache logs in the Windows Event log. So, you can be notified when certain things happen. There's also email based notification that NCache can do. So, it can send you an email when certain things happen. For example, you could set it up so if the memory consumption exceeds a certain threshold, let's say, if it grows more than 70% NCache will send you an email, or a login event.
Here's NCache manager. See that it is an explorer type of a tool. You can manage cache clusters and also the remote clients. Here is NCache monitor. It lets you view the entire cache cluster, a lot of different things about it in a very easy fashion. It's a dashboard style tool, so, you can determine what you want to see.
Important NCache Features
OK, let's come to some of the caching features that NCache has, that AppFabric does not provide. One is this thing called Dynamic Compact Serialization.
Dynamic Compact Serialization
NCache has this capability of generating serialization code for your objects at runtime and compiling it, and using it to do this serialization instead of the regular .NET serialization. You can mix and match that with regular .NET serialization. This is much faster and more compact, and it's speeds up your application.
Compression
Another feature is compression. You can specify a certain threshold. So, let's say, if an object is larger than 50k NCache will compress it if you specify it that way.
Encryption
There’s encryption. Again you can turn it On. Currently NCache provides 3DES or three DES encryption. We’re adding more encryption algorithms.
Server Configuration Options
There are a bunch of server configuration options. For example, NCache can let you use multiple network cards to improve bandwidth on the cache servers and a bunch of other features.
Absolute Expiration
Here are some caching features from a programmatic perspective, that NCache has, that AppFabric does not provide. One is called Absolute Expiration, where you can expire items on an absolute date and time, or you can say expired this ten minutes from now.
Cache Dependency
Another is Cache Dependency which is something that ASP.NET cache object has but a fabric does not support this, NCache fully supports this. There is Key Based Dependency, File Based Dependency and Custom Dependency. In Key Based Dependency one cache item depends on another. Let's say A depends on B, if B is ever updated or removed, A is automatically removed. The same goes with File and Custom.
Synchronization with Database
There's a synchronization with the database feature. With NCache there are two different ways, one is called SQL Dependency where NCache uses .NET events to synchronize the cache with SQL Server 2005-2008 or Oracle on Windows. The other is polling based dependency, which works with any OLEDB compliant database. Again this allows NCache to directly talk to your database, and synchronize the cache if corresponding data changes in the database.
Dynamic Read-Through, Write-Through and Write-Behind
Another feature is Dynamic Read-Through, Write-Through and Write-Behind. Now Read-through, Write-Through is provided in AppFabric, but NCache has a much powerful Read-through, Write-Through mechanism. Very dynamic and easy to handle. Write-Behind is something where the cache is updated immediately, but the database updates get queued up, and that queue actually gets replicated across multiple cache servers. So that, if any one cache server goes down the queued is not lost.
Cache Loader
Another feature is cache loader which you can implement, and it's called by NCache when the cache starts. So, you can basically pre-populate the cache with the cache loader.
Item Locking
Another feature is item locking, where you can lock a certain item, and nobody can read or write that item until you unlock it or the lock expires.
Bulk Operations
Another feature is Bulk Operations. This is a very useful feature for performance. Let's say if you wanted to fetch 1,000 items from the cache, and you knew all the keys, you can fetch them all in one call, instead of making 1,000 different calls.
Group/Subgroup & Named Tags
There's a grouping, and an tagging feature. Now tagging is there in AppFabric, NCache also has it, but NCache also has named tags, which are really good. Let's say, if you're storing an XML document, you could specify your own name tags. So, there is a key and value concept, and then later on search based on those key value things, and grouping of course. There's a group and subgroup concept. So, you can get everything that belongs to a group.
Searching with Object Query Language & LINQ
There’s a searching feature in NCache. NCache has an SQL type of a query language it's called OQL or Object Query Language. NCache also provides integration with LINQ. So, you can search NCache either directly through OQL or through LINQ, and do something like ‘select customers where customer.city = New York, and NCache will give you all those customers back.
Streaming API
There's a streaming API for large objects. So, that you can read chunks of them and stream back to your clients.
Event Notifications
NCache also has very powerful Event Notifications, much more so than what AppFabric has. There's key based events which are separate for Add, Update or Delete. There's also general-purpose notifications. So, you will be notified whenever anything is added inserted or removed. These are three different notifications. This feature is turned off by default, but you can turn it on because it can take up a lot of traffic. So, unless you have a use for it, we've kept it turned off.
There's a custom notification which is really very powerful. It allows your application to fire a custom event into NCache, so then NCache will propagate that event to all of the other clients connected to the cache. This allows your multiple applications to coordinate data sharing at runtime.
Continuous Query
There is a continuous query feature. This is like the SQL Dependency on the cache itself. So, you specify a SQL type of a query, let's say, again ‘select customer where customer.city = New York’, and NCache will monitor that data set. So, if any customer is added, updated or deleted with that criteria NCache will notify you.
Level 2 Cache Provider for NHibernate and Entity Framework
NCache has a Level 2 or L2 Cache provider for NHibernate and Entity Framework. NHibernate is an open source OR Mapping Engine, and an Entity Framework is a Microsoft OR Mapping Engine.
Native Java Support in NCache
Another area that NCache has is a native Java support. The Java API is 100% equivalent to .NET, and it's completely native. That means your applications can run on any UNIX platform, and can talk to the same cache cluster that .NET applications are talking to. There is no interoperability. Both .NET and Java clients use the same socket level protocol to talk to the cache.
There is runtime data sharing between Java and .NET application through NCache. NCache uses a binary format that is compatible between both Java and .NET, so, it's superfast. It doesn't have to do any XML based transformation.
There are common event notifications. So, a .NET application can fire an event and the Java application can catch it. You can also write your read-through and write-through handlers in Java. You can also write your cache loader in Java. NCache also does Dynamic Compact Serialization for Java. So, it will generate that serialization code at runtime compile it, and run it, just like the .NET Dynamic Compact Serialization. NCache can use the NCache manager for Java libraries also.
This is the end of my presentation. Let me quickly show you what you can do. You should actually go to our web site, and go to this short product videos section, and be sure to watch this NCache architecture and caching topologies video and the 5 steps to getting started video. These are very useful videos, and please go ahead and download the NCache Enterprise, either 32-bit or 64-bit. It's a fully working 30-day trial that you can use. Thank you very much.