In modern application development, achieving high performance and scalability are crucial. One effective way to enhance application responsiveness is through caching. It minimizes redundant computations and reduces database access by storing frequently accessed data in memory. .NET provides various caching mechanisms, and this document offers an overview of .NET caching, its benefits, and its practical implementations, using NCache as an example.
Key Takeaways
.NET Caching Maximizes Performance: Caching stores frequently accessed data in-memory, significantly reducing database latency and redundant computations.
Distributed Caching Ensures Scalability: Unlike in-process caching, distributed solutions like NCache allow .NET applications to scale linearly by sharing a unified cache cluster across multiple server instances.
The Cache-Aside Pattern: The most effective way to implement NCache is using the Cache-Aside pattern, where the application checks the cache first and falls back to the database only on a “cache miss.”
High Availability & Consistency: Distributed caching guarantees that data remains consistent and available across all application nodes, preventing data loss even if individual servers fail.
Reduced Infrastructure Costs: By offloading read-heavy traffic from the primary database, caching extends the lifespan and efficiency of existing database infrastructure.
What is .NET Caching?
This is a technique that temporarily stores data in a high-speed storage layer to optimize performance. It is vital in reducing latency and improving throughput in .NET applications. There are different approaches available in .NET:
- Distributed Caching: Suitable for scalable applications, distributed caching allows multiple application instances to access shared cache storage, ensuring data consistency and high availability.
- Response Caching: A technique in ASP.NET Core that stores HTTP responses for improved performance in web applications.
- Output Caching: Used in to cache the output of specific controllers or pages in web applications.
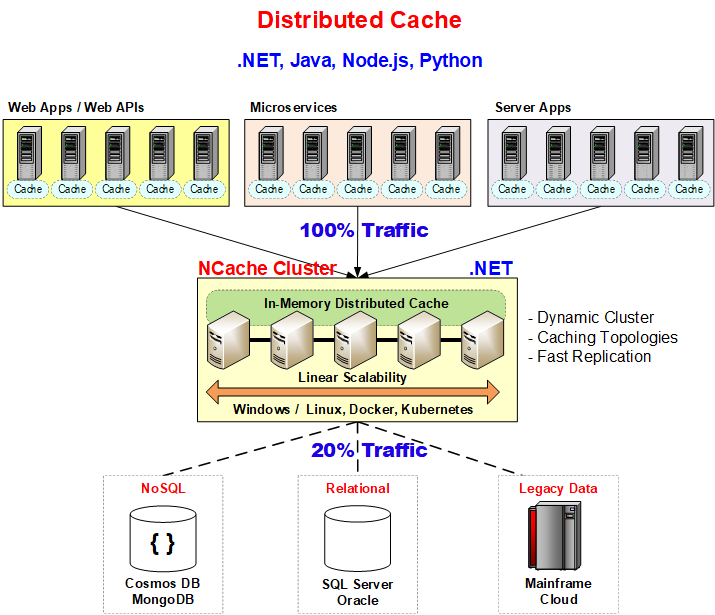
Figure: NCache Functionality.
Benefits of Caching in .NET Applications
Implementing this approach offers several advantages:
- Improved Performance: Caching reduces the need to fetch data from the primary data source, leading to faster responses.
- Reduced Database Load: Since frequently accessed data is stored in cache, the database experiences fewer queries, increasing efficiency.
- Scalability: Distributed caching solutions help applications scale by offloading work from databases and handling increased user traffic.
- High Availability: Cached data remains accessible even if the primary data source is temporarily unavailable.
Implementing Caching in .NET
NCache is a native .NET distributed cache, which makes it ideal for implementing caching in .NET applications. Here’s how caching can be integrated into such application:
1. Using NCache
NCache is a powerful distributed caching solution, particularly in ASP.NET Core environments, where it plays a crucial role in optimizing web application performance. Here’s how to configure it:
|
1 |
ICache cache = CacheManager.GetCache("demoCache"); |
2. Caching Data Using NCache
The following code snippet demonstrates how to utilize it:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 |
public class CacheService { private readonly ICache _cache; private readonly IDataRepository _repository; public CacheService() { _cache = CacheManager.GetCache("demoCache"); _repository = new DataRepository(); } public async Task GetCustomer(int customerId) { string cacheKey = $"customer_{customerId}"; // 1. Attempt to retrieve data from NCache first (Cache Hit) Customer customer = await _cache.GetAsync(cacheKey); if (customer == null) { // 2. Fetch from Database if not found in cache (Cache Miss) customer = await _repository.GetCustomerByIdAsync(customerId); if (customer != null) { // 3. Add to NCache for future requests (Cache Population) var options = new CacheItemOptions().SetAbsoluteExpiration(DateTime.UtcNow.AddMinutes(10)); await _cache.InsertAsync(cacheKey, customer, options); } } return customer; } } |
Conclusion
Caching is a fundamental optimization technique that significantly enhances the performance and scalability of such applications. While .NET provides built-in caching solutions, using NCache further improves efficiency and ensures high availability. By leveraging caching strategies effectively, developers can create robust applications which handle high traffic loads with optimal response times.
For further details, refer to the official .NET and NCache documentation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How does .NET caching improve application performance?
.NET caching improves performance by storing data in high-speed memory, which eliminates the need to repeatedly fetch the same information from a slow disk-based database. This drastically reduces network latency and improves the application’s response time (throughput).
What is the difference between standard .NET caching and NCache?
Standard .NET caching (like IMemoryCache) is typically “in-process”, meaning data lives on a single server. NCache is a “distributed cache,” meaning the data is synchronized across a cluster of servers. This makes NCache suitable for high-traffic, multi-server environments where data consistency and failover support are required.
When should I use distributed caching in my .NET application?
You should use distributed caching when your application runs on multiple servers (a web farm or microservices) and needs to share data between them. It is also essential when you need your application to scale out to handle increased traffic without bottling up your database.