Hibernate Second Level Cache
Hibernate is a popular open source Object-Relational Mapping solution for Java. For the purpose of increasing performance, Hibernate also provides the feature of caching. Hibernate provides two types of caching, First Level Cache and Second Level Cache.
The First Level Cache is built in and used as a default but, it is limited in use, not accessible, and is an in-process cache only. The Second Level Cache provides a pluggable architecture, meaning a third-party cache can be used as the Second Level Cache for Hibernate.
NCache implements the Hibernate Second Level Cache provider, offloading database execution and minimizing SQL traffic. This allows for direct configuration without code changes, granting your application immediate access to NCache’s robust suite of distributed caching features.
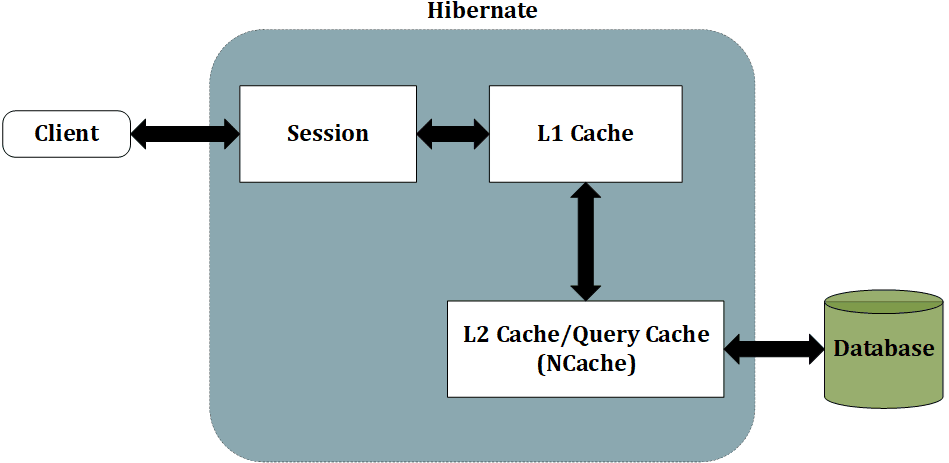
Setup NCache as Second Level Cache for Hibernate
Setting up NCache as the Second Level Cache for Hibernate is quite easy. No changes to the actual code are required. Only the configuration files need to be edited.
Now to add NCache as Second Level Cache for Hibernate, the hibernate.cfg.xml has to be edited in the following way:
- 2nd Level cache has to be enabled by setting the hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache property as true.
- NCache has to be configured as Hibernate’s Second Level Cache provider by setting the hibernate.cache.region.factory_class property as JCacheRegionFactory for Hibernate 3.6 and above.
Here is an example of the changes made in the hibernate.cfg.xml file:
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property>
<property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">JCacheRegionFactory</property>
...
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>Compatibility Note: This configuration is compatible with Hibernate versions 3.6 through 6.x and supports any Java environment utilizing the JCache (JSR-107) standard.
Cache Regions Configuration
Hibernate makes use of cache regions for storing objects. NCache allows the configuration of these cache regions with different properties. The NCacheHibernate.xml file is used for this purpose. This file contains all the configuration settings and options for regions and related configurations used by NCache.
Following is a sample NCacheHibernate.xml configuration file where regions are configured:
<configuration>
<application-config application-id="myapp" enable-cache-exception="true" default-region-name="DefaultRegion" key-case-sensitivity="false">
<cache-regions>
<region name="hibernator.BLL.Customer:Customer" cache-name="myPartitionedcache" priority="BelowNormal" expiration-type="Absolute" expiration-period="8"/>
<region name="DefaultRegion" cache-name="myPartitionedcache" priority="default" expiration-type="none" expiration-period="0" />
</cache-regions>
...
</application-config>
</configuration>Database Synchronization Configuration
NCache is a versatile, efficient, and effective distributed cache for .NET Framework, .NET Core, and Java. It comes with a broad set of features and functionalities. One of these features is database synchronization through SQL dependency. This is where the cache checks the database for any changes, and reloads or removes the items which are found to be outdated or redundant.
NCache leverages Native Database Notifications (such as SQL Dependency or Oracle Dependency) to synchronize the Hibernate L2 Cache. This ensures that if a third-party application modifies the database, NCache automatically invalidates or reloads the affected Hibernate entities. To enable this functionality, apply the following changes to the NCacheHibernate.xml file:
<configuration>
<application-config application-id="myapp" enable-cache-exception="true" default-region-name="DefaultRegion" key-case-sensitivity="false">
...
<database-dependencies>
<dependency entity-name="hibernator.BLL.Customer" type="oracle" sql-statement="select ContactName from Customer where CustomerID ='?'" cache-key-format="hibernator.BLL.Customer#[pk]" connection-string="Your Connection String"/>
</database-dependencies>
</application-config>
</configuration>Hibernate Query Cache Configuration
Hibernate provides a feature of query caching. Here the results of the queries are cached in the Second Level Cache. NCache allows you to cache such queries using this feature. This feature can be enabled by editing the hibernate.cfg.xml file in the following way:
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
...
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_query_cache">true</property>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>Enabling query cache does not cache each query by default. Instead queries needed to be cached are to be set cacheable in code. To set a query cacheable, call setCacheable(true) function of query while creating query. The code below is an example showing a cacheable query:
List customerEnumerator = session.createQuery("from Customer c").setCacheable(true).list(); Benefits of Using NCache as Second Level Cache for Hibernate
The following are the main reasons why NCache is a suitable option to be used as a Second Level Cache for Hibernate where the application is running in a multi-server environment.
- Linear Scalability of the Cache for Java Applications: NCache enables linear scalability by allowing you to add cache servers to the cluster at runtime. This architecture increases both storage capacity and transaction throughput, ensuring that your Hibernate application maintains performance as user load grows.
- High Availability via Distributed Caching Topologies: NCache is a very flexible cache, meaning that it provides its users with a rich set of caching topologies such as, Mirror Topology, Replicated Topology, Partition topology, and Partition of Replica Topology. Each topology caters to a specific scenario and need, thus making it flexible.
- Database Synchronization: You have the option to synchronize your cache with database such as SQL Server, Oracle, etc. By doing so the cache checks the database for any changes and removes or keeps items in the cache based on that change. This ensures that your cache contains items which are always up to date.
- Non-blocking Asynchronous Operations for Reduced Latency: Asynchronous operations are available in NCache. These operations allow you to work on your application without waiting for the cache to be updated, thus making everything fast. These operations can be enabled with Hibernate.
What to Do Next?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache property in your hibernate.cfg.xml and setting the hibernate.cache.region.factory_class to JCacheRegionFactory. This setup requires no changes to your application code.hibernate.cache.use_query_cache property to true in your configuration file and mark specific queries as cacheable in your Java code using the setCacheable(true) method.