Split Brain Cluster Recovery for 100% Uptime
NCache is an extremely fast and scalable in-memory distributed cache for .NET, Java, Python, Node.js. It is widely used in production for mission-critical applications. To guarantee high availability and 100% uptime, NCache provides a rich set of high availability features. One of those features is its ability to detect and resolve Split Brain in a cluster to prevent any downtime.
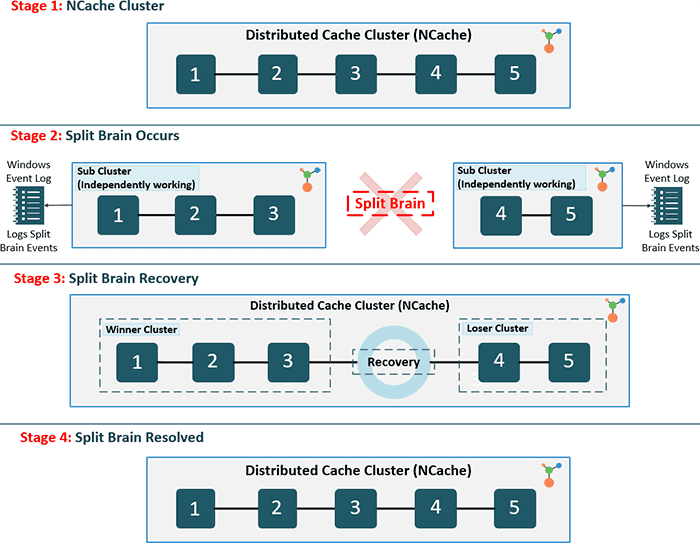
What is a Split Brain Cluster?
NCache creates a self-healing dynamic cache cluster consisting of multiple servers that talk to each other through TCP. All cache servers are interconnected in the cluster. Its membership is maintained at runtime and shared with both servers and clients.
However, like any distributed system, the NCache cluster can face a situation where one or more cache servers are disconnected from rest of the servers in the cluster, while still running. This usually occurs due to network glitches.
When this happens, each set of cache servers consider themselves the surviving servers of the original cache cluster and assumes the other cache servers have gone down. Hence, the term Split Brain, which in medical terms means that left side of the brain is unaware of the right side of the brain. The cache clients may also be split in similar fashion or they may continue to talk to all the cache servers based on the original cluster membership.
Without an automated recovery mechanism, split-brain scenarios lead to data inconsistency and integrity conflicts, as two independent sets of clients update different versions of the same data simultaneously.
This leads to errors in cache operations and most importantly data integrity problems. Each "split cluster" now has its own copy of data that is being independently updated by the clients. And, you end up with two or more copies of the same data being updated without any synchronization, causing inconsistencies.
How NCache Detects Split Brain in Distributed Clusters?
NCache has the ability to automatically detect when a Split Brain cluster occurs. Normally, the cache administrator uses the NCache Management Center or the necessary PowerShell cmdlet to remove a cache server from the cluster these events are logged. Therefore, in the case of a split brain, each sub-cluster logs events to the Windows Event Log indicating that some of its original members have left. So, in case of a Split Brain, the NCache administrator sees "node left" events for almost all the cache servers and attempts to reconnect with the "lost servers".
It is only when the network connection between the split sub-clusters is restored that it discovers a Split Brain has occurred. Upon which, each sub-cluster logs events in the Windows Event Log and also notifies the cache admin through an Email Notification that a Split Brain has occurred.
How Does NCache Split Brain Auto-Recovery Function?
Enable Split Brain recovery through config.ncconf by adding the <split-brain-recovery> tag under the <cache-settings> tag. The tag when set to True, can detect possible cluster split-brain issues. However, it is only in Partition-Replica topology.
<cache-settings...>
<split-brain-recovery enable="True" detection-interval="60"/>
</cache-settings>During the detection phase, NCache uses TCP-based heartbeats to monitor node health. If a network partition occurs, the cluster identifies the split based on the configured detection-interval. Once detected, NCache applies the Majority-node rule or the Complex-cluster rule to determine the "Winner."
NCache determines the Winner Cluster based on these criteria:
- Majority Rule: The sub-cluster with the highest number of nodes is designated the winner.
- Complexity Rule: If node counts are equal, the sub-cluster with the most complex internal configuration and connectivity wins.
If the user has configured auto-recovery in a split brain scenario, then all the sub-clusters negotiate with each other to determine the "winner". After this is done, the other sub-clusters then join this cluster by throwing away their data and acting as if they’re new nodes joining an existing cluster.
The rules used to determine which sub-cluster should win are simple. It is the sub-cluster with the largest number of member nodes. And, if multiple sub-clusters have an equal number of member nodes, then the one with the smallest coordinator's IP address wins.