Multi-Site WAN Replication
Your application may be deployed to multiple data centers, either for disaster recovery or for geographical load balancing. In such cases, your application must use a distributed cache that supports WAN replication for high availability of data in case of disaster.
NCache provides a Bridge feature to handle WAN Replication between distributed caches. It performs asynchronous replication of data to avoid any performance degradation. Moreover, the bridge itself runs as a 2-node cluster for high availability.
Bridge Topology Quick Facts
- Multi-Region Scalability: Support for 3+ active data centers.
- Zero Performance Lag: 100% asynchronous WAN replication.
- High Availability: 2-node self-healing bridge cluster.
- Conflict Management: Customizable C# logic or Last-Update-Wins.
Active-Passive Configuration
NCache enables Disaster Recovery (DR) by asynchronously replicating data from a primary active site to a standby passive site via the Bridge. You may have one active and one passive data center primarily for disaster recovery purposes. In this configuration, the active site contains the bridge and caches, while the passive contains only the caches. The active site asynchronously replicates the data through the bridge to the passive site, which acts as backup in case of disaster.
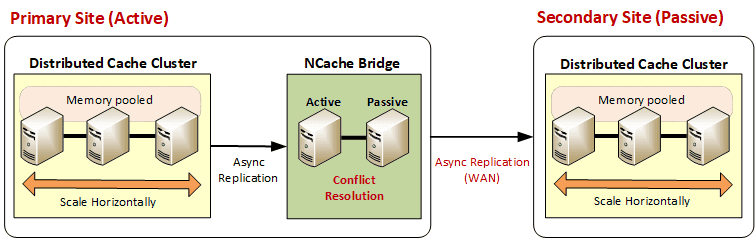
Active-Active Configuration
For regional load balancing, Active-Active topology enables multiple data centers to serve live traffic while staying synchronized in real-time. You can configure two active data centers for regional load balancing with built-in disaster recovery. One of the active sites contains the bridge and caches, while the other has caches only, similar to the active-passive configuration. However, the difference in this case is that both sites replicate data with one another as they are both actively serving client operations.
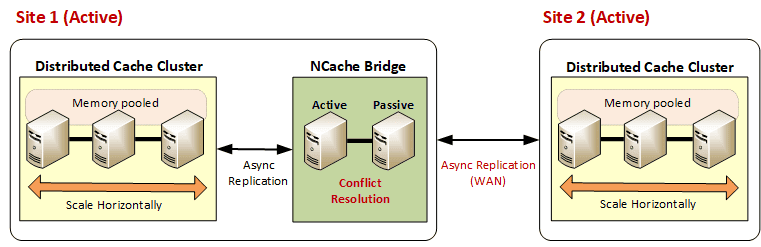
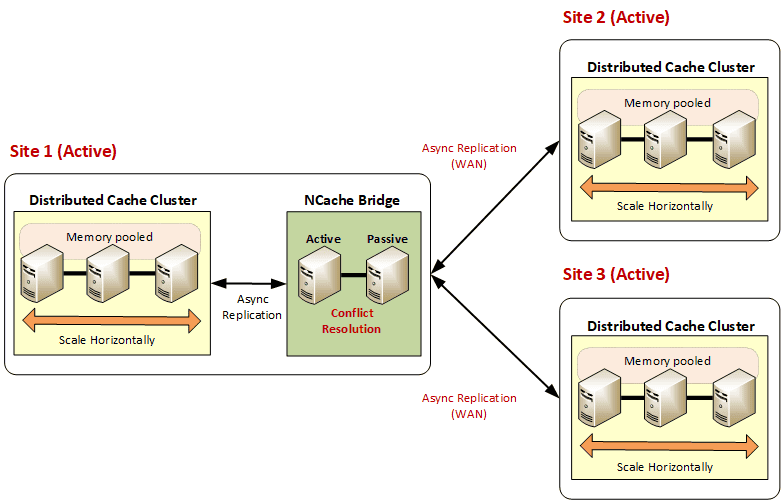
Handling 3+ Active-Active Datacenters
NCache supports complex hub-and-spoke models, allowing three or more geographic locations to share data through a centralized bridge cluster. Apart from the aforementioned configurations, NCache also supports three or more data centers. In this case, one of the sites is a bridge site which contains the bridge and caches. The other sites only contain caches. All the non-bridge sites are connected to the bridge site, so data is replicated to all sites simultaneously. You can also create a backup bridge on any of these sites to ensure high availability in case the bridge site goes down. For more details on this configuration, you can head over to the blog Understanding Multi-Datacenter WAN Replication.
Conflict Resolution in Active-Active
When you have multiple active sites, there is a chance that the same data could be updated simultaneously on each of those sites. By default, the conflict is resolved in NCache using the "last-update-wins" logic. However, you can also specify a custom conflict resolution handler that resolves the conflict by analyzing the data based on your logic.
The following code snippet shows a simplified implementation of the conflict resolver which is implemented on the cache:
public class Resolver : IBridgeConflictResolver
{
public void Init(System.Collections.IDictionary parameters) {. . .}
public ConflictResolution Resolve(ProviderBridgeItem oldEntry, ProviderBridgeItem newEntry)
{
var conflictResolution = new ConflictResolution();
switch (oldEntry.BridgeItemVersion)
{
case BridgeItemVersion.OLD: { /* Replace Item with New Entry */ }
break;
case BridgeItemVersion.LATEST: { /* Keep Old Entry */ }
break;
case BridgeItemVersion.SAME: { /* Your custom logic */ }
break;
}
return conflictResolution;
// Configure this implementation on cache
}
public void Dispose() {. . .}
}For more details on conflict resolution, you can refer to Conflict Resolution Docs.
Parallel & Bulk Async Replication
Replication across regionally distributed sites can result in performance degradation because of latency. Unlike standard synchronous replication which causes high latency, NCache Bridge uses asynchronous queuing to decouple application performance from WAN speed. NCache Bridge replicates data asynchronously across all data centers, ensuring no application downtime.
Moreover, the bridge also sends multiple data items as a single bulk request to the other site, drastically reducing network trips across the WAN. This bulk replication mechanism is more efficient than item-by-item transfer, reducing network overhead by grouping multiple updates into a single TCP request. As an add-on, the bridge has built-in replication as well: it is a 2-node cluster which self-replicates so it is highly available itself. For more details on NCache bridge behavior, you can refer to the NCache Bridge Architecture Docs.
Handling Disaster at Runtime
NCache seamlessly handles disaster situations in each of the aforementioned data center configurations.
- Active-Passive: If the passive site goes down, the active site continues to serve client operations without replication until the passive site comes back up. Once the passive site recovers, the passive site resyncs itself, and WAN replication takes place. If the active site goes down, the traffic is routed to the passive site which temporarily acts as an active site as it is synchronized with the active site. Once the original active site is restored, it resynchronizes itself and becomes active again.
- Active-Active: In this case, if the active site goes down, the traffic is routed to the other site which continues to serve the clients seamlessly, as it is also an active site. Once the original site comes back, it resyncs itself automatically and WAN replication continues.
- 3+ Active-Active:
The following cases might occur:
- Non-bridge active site goes down: The other sites continue to replicate one another and the traffic on this site is rerouted to the other connected sites without interrupting the users.
- Bridge active site goes down: If the bridge active site goes down, it means that the WAN replication will not take place as the bridge is also down. So, one of the other running active sites temporarily acts as a bridge site. You can also create a backup bridge on one of the sites for such scenarios. Since NCache allows caches to connect to a bridge at runtime, there is no downtime at the client end. Once the original site is back, it automatically resyncs itself, and the traffic is routed to this site, just as before.
What to Do Next?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
IBridgeConflictResolver interface to apply your own business logic based on the data versions.