Performance and scalability are of paramount importance in modern software applications. Caching serves as an essential technique that improves application responsiveness while minimizing database load. Distributed caching, specifically, ensures high availability and reliability by storing data across various servers. NCache, a robust and fully native .NET distributed caching solution, offers developers the ability to optimize their applications for speed and efficiency.
Key Takeaways
Scalability & Performance: Distributed caching stores data in-memory across multiple servers, drastically reducing latency and allowing applications to scale linearly by adding nodes at runtime.
High Availability: NCache eliminates single points of failure by replicating data across the cluster, ensuring 100% uptime and zero data loss even during server outages.
Database Optimization: By handling frequently accessed data in the cache layer, applications significantly reduce database bottlenecks and operational costs.
Advanced .NET Features: Provides a native .NET solution with powerful capabilities like SQL-like querying, LINQ support, and automated Read-Through/Write-Through providers.
Why Use Distributed Caching?
Traditional caching solutions store data in a centralized location, resulting in bottlenecks and potential failures. In contrast, distributed caching distributes data across multiple servers, offering the following benefits:
| Feature | Traditional / In-Process Cache | Distributed Cache (NCache) |
| Scalability | Limited (Bound by single server resources) | Unlimited (Horizontal scaling at runtime) |
| Availability | Low (Data is lost if the application restarts) | High (Replicated data survives failures) |
| Reliability | Single point of failure risks | Zero data loss (Automatic failover support) |
| Performance | High speed, but creates database bottlenecks | Sustained speed (Offloads database queries) |
- Enhanced Response Times: Stores data in-memory for fast access. NCache also provides a Client Cache feature, which retains frequently accessed data on the application server, further minimizing latency by eliminating network round trips to the distributed cache.
- Scalability: Enables applications to handle higher traffic volumes by distributing load among multiple cache servers. Due to its distributed nature, additional cache nodes can be integrated seamlessly as demand increases without impacting performance. NCache’s ability to scale horizontally at runtime ensures that applications maintain consistent performance even during peak loads.
- High Availability: Ensures data remains accessible, even in case of server failures. NCache accomplishes this by replicating cached data across various servers, so if one server fails, another server immediately takes over. This eliminates single points of failure and guarantees continuous access to cached data. Furthermore, NCache supports automatic failover and data synchronization to uphold data consistency across nodes.
- Reduced Database Load: By caching frequently accessed data, the number of database queries is significantly reduced.
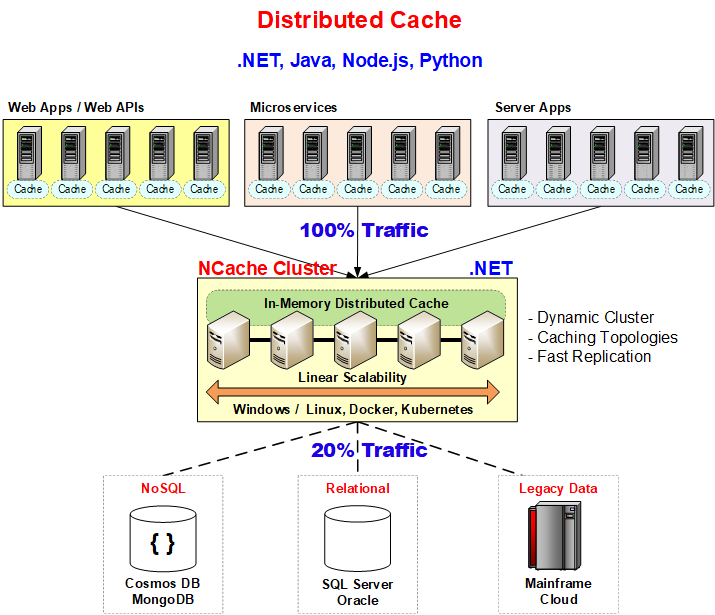
Figure 1: Distributed Caching in .NET
Distributed Caching Overview
Distributed caching enables applications to store and access data across multiple servers, ensuring both high availability and improved performance. The following is an example of how to perform basic caching operations utilizing NCache.
Basic Caching Operations in NCache
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
using Alachisoft.NCache.Client; using System; class Program { static void Main() { ICache cache = CacheManager.GetCache("myCache"); string key = "item1"; object value = cache.Get(key) ?? FetchFromDatabase(key, cache); Console.WriteLine("Data retrieved: " + value); } static object FetchFromDatabase(string key, ICache cache) { object value = "Fetched from database"; // Insert the fetched data into the cache for future requests cache.Insert(key, value); return value; } } |
This example demonstrates adding, retrieving, and updating a cache entry using NCache.
Key Caching Features
NCache offers several advanced caching features that help enhance performance and manageability:
Data Grouping and Tagging
With Groups, Tags, and Named Tags, NCache allows developers to logically organize cached data, facilitating efficient bulk operations.
SQL-Like Queries and LINQ Support
NCache supports complex searches within cached data utilizing SQL-like queries or LINQ, simplifying the retrieval of objects based on attributes. The following example demonstrates how to perform an SQL-like query to retrieve objects.
Example: Executing an SQL Query in NCache
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
using Alachisoft.NCache.Client; using Alachisoft.NCache.Runtime.Caching; using System; using System.Collections; class Program { static void Main() { ICache cache = CacheManager.GetCache("myCache"); string query = "SELECT * FROM Employees WHERE Department = ?"; Hashtable parameters = new Hashtable { { "Department", "IT" } }; ICacheReader reader = cache.Search(query, parameters); while (reader.Read()) { Console.WriteLine("Employee: " + reader["Name"]); } } } |
Read-Through and Write-Through Caching
NCache also supports Read-Through and Write-Through caching, facilitating efficient data access and storage. Read-Through enables applications to automatically retrieve data from the database in the event of a cache miss. Whereas, Write-Through updates the database whenever cached data is updated in the database. This approach minimizes direct interactions with the database while maintaining data consistency.
Getting Started with NCache
To integrate NCache into your .NET application, follow these steps:
- Download and Install: Visit the NCache download page to get the latest version and set up the caching environment.
- Install the NuGet Package: Add NCache to your .NET application using NuGet:
|
1 |
Install-Package Alachisoft.NCache.SDK –Version x.x.x |
-
- This ensures you have the latest NCache client library installed.
- Configure NCache in Your Application: Set up your cache connection and caching policies according to your application needs. Refer to the official documentation for configuration best practices.
Conclusion
Distributed caching is a crucial strategy for enhancing performance, scalability, and reliability of .NET applications. NCache offers a comprehensive caching solution with powerful features, making it the ideal choice for your high-traffic .NET applications. Start using NCache today to leverage its advanced capabilities and boost your application’s efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: When should I use distributed caching instead of a database?
A: Use distributed caching for read-intensive data that doesn’t change frequently (e.g., product catalogs, user sessions) to reduce database trips and latency. This allows the application to serve data from fast memory rather than slow disk I/O.
Q: Does distributed caching work with microservices?
A: Yes, it is the preferred state management solution for microservices. It allows independent services to share data consistently and remain stateless, preventing the tight coupling that occurs with shared databases.
Q: How does NCache handle server failures?
A: NCache replicates data across multiple nodes in real-time. If one server fails, a replica immediately takes over, ensuring zero data loss and 100% high availability without disrupting the application.
Q: Can I search the cache using SQL or LINQ?
A: Yes. Unlike simple key-value stores, NCache allows you to query cached data using standard SQL-like commands or LINQ. This lets you retrieve specific objects based on attributes (e.g., “Select * From Products Where Category = 'Electronics'“) without reloading the entire collection.