With the increasing demand for high-performance and scalable applications, distributed caching has become a necessity. It enhances application speed and responsiveness. But when multiple clients access and modify data concurrently, the cache and database lose synchronization. This is typically addressed through expiration mechanisms like Time-to-Live (TTL) or Absolute Expiration which removes cache items after a certain time. While this mechanism helps, it’s based on the assumption for how long the data remains unchanged, leading to the possibility of stale data.
Key Takeaways
- Prevent Stale Data: Use SQL Dependency to automatically invalidate cache items when SQL Server data changes.
- Event-Driven: Relies on SQL Server Query Notifications to trigger updates in real-time.
- Auto-Reload: Combine with NCache ReadThru Provider to automatically fetch fresh data after invalidation.
- Optimization: Supports parameterized queries and stored procedures for better performance and reduced compilation overhead.
For data that doesn’t change often or is not critical, expiration-based caching might be an option. In contrast, for data sensitive to business operations where outdated information can cause financial or operational issues, stale cache data is a big risk. In these cases, an effective cache synchronization mechanism is required.
| Feature | Time-to-Live (Expiration) | NCache SQL Dependency |
| Data Freshness | Data may become stale before expiration. | Always Fresh: Updates in real-time. |
| Trigger Mechanism | Fixed time duration. | Event-Driven: Triggered by SQL Server changes. |
| Performance | Minimal overhead. | Slight overhead due to database notifications. |
| Best Use Case | Static or reference data (e.g., Country lists). | Critical transactional data (e.g., Inventory, Price). |
How Synchronizing NCache with SQL Server Works?
To keep the cache synchronized with the database, NCache provides a feature called SQL Dependency. This uses SQL Server Query Notifications to invalidate cache items when their corresponding database records change to avoid any outdated data.
Query Notifications in SQL Server
Query Notifications is a SQL Server feature that alerts registered clients whenever specific dataset changes occur. NCache Server registers itself as an SQL Server client using SQL Dependency, allowing automatic synchronization between the cache and database.
- Subscription: NCache registers a query with SQL Server to monitor specific data.
- Detection: SQL Server detects a change in the subscribed dataset.
- Notification: SQL Server sends a query notification event to NCache.
- Invalidation: NCache immediately invalidates the outdated cached item.
- Reload: The next time the application requests that data, it retrieves a fresh copy from the
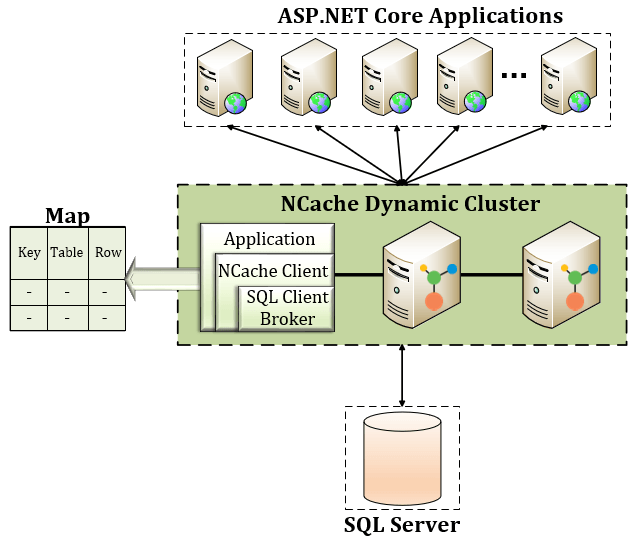
Implementing SQL Dependency in .NET 8 with NCache
NCache provides a SQL Dependency API to register cache items for automatic invalidation. To enable this feature, you need to pass the following parameters when adding data:
- Connection String: Defines the SQL Server connection.
- CommandText: Specifies the SQL query being monitored.
Example: Synchronizing Cache with SQL Server in .NET 8
Consider a .NET 8-based online shopping platform where thousands of customers browse products simultaneously. On Christmas Day, a 40% discount is applied across the entire catalog. If the application cache does not reflect this update, customers might see incorrect prices, causing frustration.
With NCache SQL Dependency, the cache remains synchronized with the database, ensuring accurate pricing information.
The following C# code demonstrates how to initialize the SqlCacheDependency object with a connection string and a specific SQL query, then attach it to a CacheItem.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
// Define the connection string to SQL Server string connectionString = "Server=SERVERNAME; Database=NORTHWIND; User Id=USERID; Password=PASSWORD;"; // Fetch products from the database List products = FetchProductsFromDB(); // Create a dictionary to store cache items Dictionary<string, CacheItem> cacheItems = new(); foreach (Product product in products) { string productKey = $"Product:{product.ProductID}"; string query = $"SELECT UnitPrice FROM dbo.Products WHERE ProductID = {product.ProductID}"; // Create SQL Dependency SqlCacheDependency dependency = new(connectionString, query); CacheItem productItem = new(product) { Dependency = dependency }; cacheItems[productKey] = productItem; } // Add products to NCache cache.AddBulk(cacheItems); |
Auto-Reload Cache with ReadThru Provider
To maintain up-to-date entries following a database update, consider utilizing NCache’s ReadThru Provider to automatically refresh the cache. This approach guarantees that the cache always contains the latest data, eliminating the need for the application to manually retrieve it.
To enable auto-reloading, modify your caching logic as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
// Create a new cache item with SQL dependency CacheItem item = new(product); item.Dependency = sqlDependency; // Enable automatic cache resynchronization item.ResyncOptions = new ResyncOptions(true); // Add the cache item with Resync enabled cache.Insert(key, item); |
Optimizing Cache Synchronization with Parameterized Queries
Frequent database updates can cause cache invalidations which impacts performance. SQL Server 2022 has optimizations for parameterized queries, which reduces query compilation overhead. NCache leverages these optimizations by allowing precompiled queries with parameters, improving efficiency.
Example: Using Parameterized Queries
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
// Define SQL parameters SqlCmdParams paramProductID = new() { Type = CmdParamsType.Int, Value = product.ProductID }; Dictionary<string, SqlCmdParams> parameters = new() { { "@ProductID", paramProductID } }; // Create SQL Dependency with parameterized query SqlCacheDependency dependency = new(connectionString, query, SqlCommandType.Text, parameters); CacheItem productItem = new(product) { Dependency = dependency }; cache.Add(productKey, productItem); |
Stored Procedure-Based SQL Dependency
Many enterprises prefer using stored procedures for database interactions due to their efficiency and maintainability. NCache supports Stored Procedure-Based SQL Dependency, allowing organizations to register cache synchronization based on stored procedure execution.
Example: Creating a Stored Procedure for SQL Dependency
|
1 2 3 |
CREATE PROCEDURE sp_GetUnitPriceByProductID @ProductID INT AS SELECT UnitPrice FROM dbo.Products WHERE ProductID = @ProductID; |
Example: Using Stored Procedure in .NET 8
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
// Specify the stored procedure name string spGetUnitPriceByProductID = "sp_GetUnitPriceByProductID"; // Create SQL Dependency with Stored Procedure SqlCacheDependency dependency = new(connectionString, spGetUnitPriceByProductID, SqlCommandType.StoredProcedure, parameters); CacheItem productItem = new(product) { Dependency = dependency }; cache.Add(productKey, productItem); |
Conclusion
If you are building high-performance ASP.NET 8 applications, synchronizing the cache with SQL Server using NCache is a robust solution. Here’s why:
- NCache is an in-memory solution that ensures ultra-fast data access.
- No client interference is needed for auto-rebalancing, enhancing scalability.
- Seamless integration with SQL Server notifications and stored procedures.
- Eliminates stale data issues, ensuring data consistency across the application.
- Highly scalable as it adds more servers dynamically to handle increasing loads.
For applications where SQL Server does not support Query Notifications, NCache provides Polling-Based Dependency, ensuring real-time synchronization even in such environments.
Start using NCache SQL Dependency today to eliminate data integrity issues and ensure your application always serves up-to-date information.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is SqlCacheDependency in NCache?
A: It is a feature that creates a link between a cache item and a SQL Server database row. If the data in the database changes, NCache automatically removes the item to ensure data consistency.
Q: Can I use Stored Procedures with NCache SQL Dependency?
A: Yes, NCache supports registering dependencies using Stored Procedures, which is often preferred for enterprise security and performance.
Q: Does SQL Dependency require polling?
A: No. NCache uses SQL Server Query Notifications (event-based) to detect changes, avoiding the performance overhead of polling.
Q: How can I automatically reload data into NCache after a SQL Server update?
A: By using ResyncOptions with SetNeedsProviderResync(true) when adding the item. This triggers the configured Read-Through provider to fetch the latest data from the database immediately after the SQL dependency invalidates the cache item, ensuring the cache is not just empty, but updated.






