In a world where you can find an abundance of jobs like Data Analyst, Data Engineer, Database Administrator, Data Scientist, Data Architect, and more, it is clear that as a society, the collection, preservation, and analysis of data is near and dear to us. We are endlessly dependent on data, particularly in businesses. As such, companies are particularly vulnerable to hacking, natural disasters, and other forms of data loss these days.
Distributed caching is another avenue heavily dependent on data. And with these vulnerabilities prompting such uncertainty, several distributed caching platforms (like NCache & Redis) offer their customers peace of mind with their Persistence store. Persistence refers to the process of writing data in a specific location for durable storage and data backup.
Why is Persistence Necessary?
But why is such a backup necessary for distributed caching when we tend to expect volatility in such a platform? Similarly, why is this so important, given that we drive cache data from other sources?
Well, if you lose all your cache data (accidentally or intentionally, for example, via catastrophic failure or node maintenance), your application is forced to slowly reprocess all pre-existing data. Furthermore, if your trips to the original data source are costly in terms of money or time, the entire repopulation process can be a nightmare. Clearly, such a persistence store is a real benefit if our caching solution provides it. But whose solution is better?. Let’s discuss and decide.
Redis Vs. NCache Persistence Store
How Do They Work?
NCache’s entire technique for updating objects in the persistence store is asynchronous and employs a persistent queue which spares you any unnecessary waiting time. A background thread simply examines all operations in this queue (at predefined intervals) and copies them to the store as is – while you continue with your work. So, when you perform write operations, the cache loads the data into memory before adding it to the store.
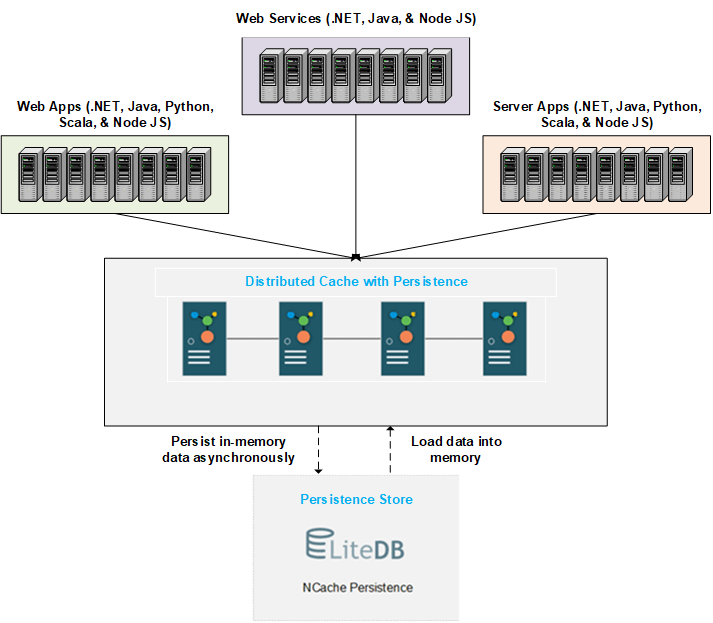
Figure: The detailed process of data persistence and loading in NCache.
On the other hand, Redis offers three different ways you can use persistence; RDB (Redis Database), AOF (Append Only File), and RDB + AOF. With RDB, they make copies of your dataset at periodic intervals. They call this process snapshotting and it works similarly to the unsaved drafts version system employed by Microsoft software.
AOF is more like an operation log. It merely catalogs any and all write operations as they take place. When used together, AOF & RDB present a complete picture of the processes taking place within a cache.
Why is NCache better than Redis?
Increased Backup-interval & Reduced Chances of Data Loss
First and foremost, NCache allows users to set an interval of their choice from a second onwards – which minimizes the chance of cache data loss. Alternatively, Redis only offers a few options for backup times (i.e., no backups, every 1 hour, every 6 hours, or every 12 hours). Additionally, Redis themselves admit that RDB is not a great choice when minimizing data loss, particularly, when dealing with Power outages, etc.
No Unnecessary Memory Consumption
NCache only creates one version of the persisted data that is constantly updated using optimized queues. This process is much more memory efficient as compared to the options Redis offers. For instance, the snapshotting process creates multiple copies of your database, which consumes memory unnecessarily. AOF files are usually even larger than their equivalent RDB files, even when considering the same dataset. While Redis claims the ability to rewrite the AOF in the background when it gets too big, even this process involves creating a brand-new file. And this rewriting would be completely unnecessary if you opt to use NCache.
Asynchronous Backup Operations
The NCache queue in works completely asynchronously, and the enqueued data does not go anywhere even when it cannot write to the persistence store at a given point in time. On the other hand, Redis employs the fsync policy to record operations for its AOF option. By default, this mechanism uses a background thread for write operations. Unfortunately, the thread can only perform these operations when no fsync is in progress.
Near Real-Time Operations & High-Availability
As we’ve discussed NCache offers users with the ability to set very short time intervals. Therefore, despite being asynchronous, the persistence of data is almost real-time, without any compromise on application performance. An observation that reiterates how there is little to no chance of data loss with NCache persistence, especially compared to Redis.
Additionally, the application can still access data that has not yet been stored in the cache cluster while it loads back into the cache cluster. If this process is yet to be completed in memory, NCache automatically reads it from the persistent storage.
Disaster Recovery
Speaking of data loss, when things go catastrophically wrong with NCache, you have access to all your data upon cache restart. Whereas with the alternative, you only have several outdated versions of the data due to the large persistence intervals.
Optimized Queues
Moreover, if two write operations take place, one to update an operation and then another to delete it, NCache’s optimized queue will simply delete it instead of performing the unnecessary update. Unfortunately, the logging process employed by Redis does not account for redundancy.
Incorporates Redis’s Strengths
Lastly, while it is observable that the persistence store is a more powerful feature in NCache, if aspects of Redis’s methodology appeal to you, we have a solution for that as well. For instance, if you are intrigued by the possibility of viewing your dataset as it was at a certain point in time, NCache offers users the option to Import/Export cache data. Similarly, it also offers extensive monitoring capability outside of just the NCache Logs (which are a more optimized version of AOF), it offers monitoring tools via the NCache Manager, PowerShell, various PerfMon tools, SNMP Counters, and third-party tools like Grafana and Prometheus.
Conclusion
Clearly, NCache offers users the best of both worlds when it comes to persistence. And that is without even mentioning the series of easy-to-manage and configure tools you’ll get as a bonus even if your primary concern is persistence. So, what are you waiting for? Download NCache now and start your 60-day free trial!






